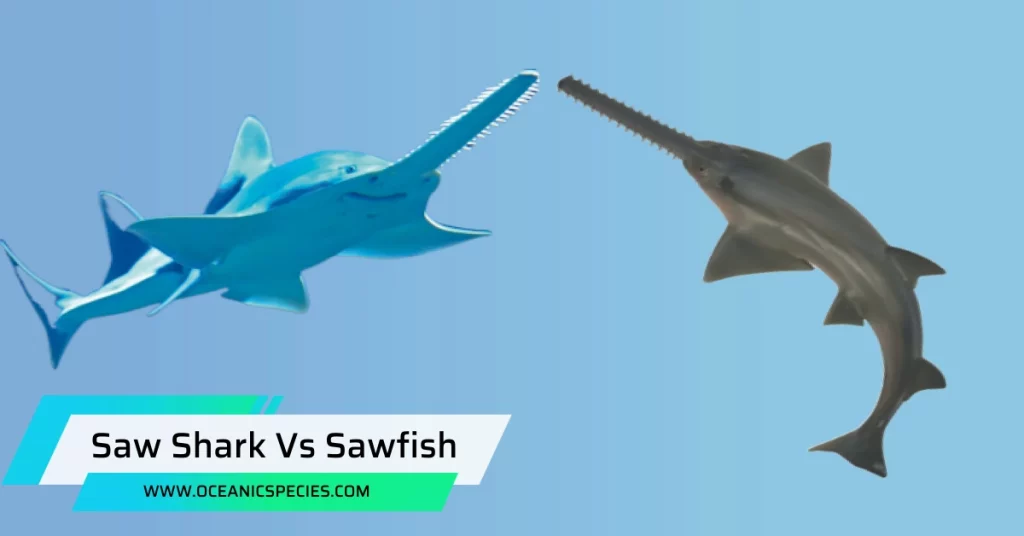
The main difference between a saw shark and a sawfish is that saw sharks have long, toothed snouts that resemble a saw, while sawfish have longer, flattened snouts with teeth only on the sides. Saw sharks belong to the family Pristiophoridae, while sawfish belong to the family Pristidae.
Saw sharks and sawfish may appear similar due to their shared feature of a long snout with teeth, but there are distinct differences between the two. Saw sharks typically have a shorter snout, with teeth that are evenly distributed along both sides of their saw-like rostrum.
Sawfish, on the other hand, have a longer and flatter snout, with teeth only along the edges of their rostrum. Saw sharks are streamlined and efficient predators, while sawfish have a more paddle-like appearance and are primarily bottom-dwellers. Despite their differences, both species have adapted to their respective environments and have unique characteristics that make them fascinating creatures in their own right.
Saw Shark: A Formidable Predator
The saw shark, also known as the sawshark or sawdogbelongs to the family pristiophoridae. With its unique and intimidating saw-like rostrum, the saw shark is a formidable predator in the underwater world. Let’s delve into its distinctive features, hunting behavior, and compare its rostrum to a sawfish’s.
Description Of Saw Shark’S Unique Features
The most distinctive feature of the saw shark is its rostrum, a long and flat snout that is lined with sharp teeth-like serrations. The rostrum can grow up to a third of the saw shark’s total body length, ranging from 8 inches to 4 feet long.

It is used primarily for hunting and defense.
Unlike other shark species, the saw shark’s rostrum is soft and flexible, allowing it to slash and swish rapidly through the water. This unique appendage not only aids in capturing prey but also helps with navigation and locating food hidden in the sand.
The saw shark’s body is slender and elongated, typically measuring between 2 and 4.5 feet in length, excluding the rostrum. It has a grayish-brown or olive-green coloration, often with a mottled pattern that provides effective camouflage in the oceanic environment.
Discussion Of Saw Shark’S Hunting Behavior
The saw shark is an opportunistic hunter that feeds on a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and crustaceans. Using its electroreceptive organs, called ampullae of lorenzini, the saw shark can detect the electrical signals emitted by its prey.
Once a potential meal has been located, the saw shark swiftly maneuvers its saw-like rostrum to stun or impale its prey before devouring it. The serrations along the rostrum ensure a secure grip on the prey, preventing it from escaping.
Saw sharks are primarily bottom-dwellers, inhabiting sandy and muddy areas along continental shelves and slopes. They use their rostrum to dig into the substrate, searching for buried prey. Although they are generally not considered aggressive towards humans, saw sharks may exhibit defensive behavior if threatened or cornered.
Comparison Of Saw Shark’S Rostrum To A Sawfish’S
While the saw shark and sawfish share a similar saw-like rostrum, there are some notable differences between the two. The rostrum of a saw shark is softer and more flexible compared to a sawfish’s, as it lacks the hard enamel covering that the rostrum of a sawfish possesses. The teeth-like serrations on a saw shark’s rostrum are more widely spaced compared to those on a sawfish’s rostrum.
Sawfish primarily inhabit freshwater habitats like rivers and estuaries, whereas saw sharks are mainly found in saltwater environments. With its extraordinary features and hunting prowess, the saw shark remains an intriguing and enigmatic creature in the realm of marine life.
Sawfish: The Saw-Wielding Hunter

Sawfish roam the depths of our oceans, equipped with a unique weapon: a saw-like nose called a rostrum. This razor-sharp tool sets them apart from other fish, making them exceptional hunters in their underwater realm. In this section, we will delve into the world of sawfish, exploring their habitat, the rostrum’s purpose, and their feeding habits.
Introduction To Sawfish And Its Habitat
Sawfish can be found in both tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They are often spotted in coastal areas, estuaries, and river systems, preferring habitats that offer a mix of salt and freshwater. These majestic creatures particularly thrive in mangrove swamps, where they can navigate through the intricate root systems and find abundant prey.
With their impressive size, reaching up to 23 feet long, sawfish command a dominant presence in these underwater ecosystems.
Detailing The Sawfish’S Rostrum And Its Purpose
The most remarkable feature of the sawfish is its elongated rostrum, which resembles a saw with either side lined with sharp teeth-like projections. This unique adaptation serves several purposes, making it an indispensable tool for their survival:
- Defense: The sawfish uses its rostrum to defend itself from predators. With swift side-to-side movements, they can inflict severe injuries on potential attackers, deterring them from causing harm.
- Sensory detection: Equipped with thousands of electroreceptors, the rostrum allows sawfish to detect the weak electrical fields produced by their prey. This advanced sensory system helps them locate hidden organisms in murky waters, giving them an advantage when hunting.
- Rooting for prey: Sawfish employ their rostrum to root around the sand or mud, dislodging hidden prey such as crustaceans, fish, and small mammals. This method is akin to a metal detector, as it stirs up the substrate and exposes potential meals.
Highlighting The Feeding Habits Of Sawfish
Sawfish are opportunistic hunters, preying on a variety of aquatic creatures. Their feeding habits include:
- Ambush predators: Sawfish adeptly hide among seagrass beds or near structures like coral reefs, waiting for unsuspecting prey to pass by. Once they spot their target, they swiftly strike with their rostrum, stunning or impaling their catch.
- Cooperative hunting: In some cases, sawfish cooperate with one another to hunt in groups. By creating a semi-circle formation, they enclose a school of fish, making it easier to catch their meal.
- Scavenging: Sawfish are not entirely reliant on hunting. They are known to scavenge on carcasses, capitalizing on available food sources to ensure their survival.
- Ingesting prey: After capturing their prey, sawfish manipulate their rostrum, positioning it vertically to facilitate swallowing. This allows them to consume larger fish or animals in manageable portions.
Saw Shark Vs. Sawfish: Anatomy And Behavior
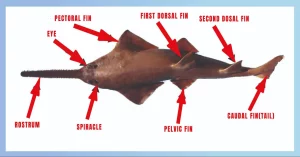
Both saw sharks and sawfish possess unique adaptations and hunting strategies that enable them to thrive in their respective environments. While their serrated rostrums serve similar purposes of capturing and consuming prey, the differences in their physical characteristics and hunting techniques highlight their distinct evolutionary paths.
Comparison Of Physical Characteristics Between The Two Species:
Saw sharks:
- Possess a long, flattened snout known as a rostrum, which is lined with teeth on both sides.
- Size varies depending on the species, with some reaching lengths of up to 6 feet.
- Have elongated bodies with a streamlined shape, allowing for swift movements in the water.
- Typically feature a brownish-gray coloration, helping them blend in with their sandy ocean habitats.
- Eyes are positioned on the sides of their heads, providing an expanded field of vision.
Sawfish:
- Also possess a long, flattened snout called a rostrum, but it is lined with teeth on only one side.
- Can grow much larger than saw sharks, with some species reaching lengths of up to 18 feet.
- Have broad bodies that are highly specialized for living in freshwater environments.
- Often display a light brown or gray coloration, aiding in camouflage in their preferred habitats.
- Eyes are positioned closer to the top of their heads, allowing for a better view of what’s above them.
Explanation Of Their Hunting Techniques And Adaptations:
Saw sharks:
- Use their unique rostrums to slash through schools of fish, stunning or injuring their prey.
- Possess electroreceptors on their rostrums, which help detect the electrical impulses emitted by potential prey in the water.
- Employ an ambush hunting strategy, waiting patiently for prey to come within striking distance before attacking.
- Agile swimmers, allowing them to quickly change direction and pursue fast-swimming prey.
Sawfish:
- Utilize their rostrums to stir up the soft bottom sediments, exposing hidden prey such as crustaceans and small fish.
- Have electroreceptors on their snouts, enabling them to detect the weak electric fields produced by their prey.
- Employ a sweeping motion with their rostrums to capture prey, often slashing sideways to injure or immobilize their victims.
- Are capable of stunning larger prey by striking them with a swift, powerful motion.
Discussion On How Their Serrated Rostrums Aid In Capture And Feeding:
Saw sharks:
- The teeth lining their rostrums are sharp and densely packed, allowing them to inflict substantial damage on their prey.
- The serrated edges of their rostrums help them to hold onto captured prey, making it difficult for prey to escape.
- By using a saw-like motion, saw sharks can effectively slice through schools of fish, making it easier to capture multiple prey items.
Sawfish:
- The teeth on one side of their rostrums are similar to small spikes, allowing them to secure their prey without it easily slipping away.
- The serrated rostrums aid in macerating prey, making it easier for sawfish to consume their meals.
- Sawfish can also exhibit cooperative feeding behavior, with multiple individuals working together to corner and capture larger prey.
Showdown: Who Is The Better Predator?
In the fierce battle of predator versus predator, both the saw shark and the sawfish display remarkable hunting abilities and impressive track records of successful hunts. While the saw shark excels in efficiency and speed, the sawfish’s versatility and adaptability make it a potent predator.
Comparison Based On Hunting Efficiency And Success Rates
When it comes to the title of the better predator, the showdown between the saw shark and the sawfish gets really interesting. Let’s take a closer look at their hunting abilities and success rates to determine who comes out on top.
Saw shark:
- Efficient hunting: The saw shark is known for its incredible hunting efficiency. Its saw-like rostrum is equipped with electroreceptors that help detect prey in murky waters.
- Successful strikes: With lightning-fast movements, the saw shark launches itself at its prey, delivering a swift and precise blow with its serrated rostrum.
- Pursuit strategy: It often chases down its prey, relying on its keen senses and speed to track and catch its target. The saw shark’s hunting tactics make it a formidable predator.
Sawfish:
- Hunting prowess: The sawfish is renowned for its hunting prowess and adaptability. Its elongated rostrum allows for efficient maneuvering and striking during hunts.
- Strategic hunting techniques: The sawfish often lays in wait, blending in with its surroundings. It strikes with precision, using its saw-like rostrum to stun or impale its prey.
- Wide prey range: Sawfish have a diverse palate, targeting various fish species, crustaceans, and even smaller sharks. This adaptability contributes to their success as hunters.
Analyzing The Prey Preferences Of Both Species
Understanding the prey preferences of the saw shark and the sawfish provides insight into their hunting strategies and overall predatory success. Let’s dive deeper into what these predators prefer on their menu.
Saw shark:
- Fish-focused diet: The saw shark predominantly feeds on bony fish, using its rostrum to tear into their flesh. Its electroreceptors enable it to detect fish hiding in the sand or under debris.
- Bottom-dwelling specialists: They are skilled at hunting prey that resides near the ocean floor, such as flatfish and small crustaceans.
- Opportunistic feeders: Saw sharks also scavenge for carcasses, taking advantage of any available food source in their habitat.
Sawfish:
- Varied prey selection: Sawfish have a diverse diet, targeting a range of aquatic organisms. From small fish like mullet and herring to larger prey such as rays, crustaceans, and even water birds, they are opportunistic hunters.
- Bottom-dwellers and open water foragers: Sawfish adapt their hunting technique according to their environment. They can be found scouring the sandy sea bottoms or actively chasing down prey in open waters.
Discussing How The Serrated Rostrums Play A Role In Their Predatory Success
The serrated rostrums of the saw shark and the sawfish play crucial roles in their predatory success, giving them an edge when it comes to hunting and catching prey. Let’s explore how these unique adaptations contribute to their effectiveness as predators.
Saw shark:
- Ripping and disabling prey: The serrated edges along the rostrum are perfect for tearing through the flesh of its prey, disabling them quickly and efficiently.
- Pinpoint accuracy: The elongated snout with its electrical receptors, combined with the sharp teeth, allows the saw shark to precisely strike its target, immobilizing it with well-aimed blows.
- Efficient feeding: The rostrum also aids in feeding by pinning the prey to the ocean floor, allowing the saw shark to devour its catch without losing it.
Sawfish:
- Stunning and impaling prey: The saw-like rostrum of the sawfish is a formidable weapon, allowing it to both stun and impale its prey during hunts. The rostrum is filled with sensory organs that aid in detecting and capturing prey.
- Versatile tool: The saw-like rostrum is highly maneuverable, assisting in prey manipulation as well as defense against larger predators. It can also be used to dig into the ocean floor in search of buried prey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Saw Shark And A Sawfish?
The main difference is that a saw shark belongs to the shark family, while a sawfish is a type of ray.
How Does The Saw Of A Saw Shark Differ From That Of A Sawfish?
The saw of a saw shark is covered in teeth that point backwards, while the sawfish has teeth that point forward.
What Purpose Does The Saw Serve For A Saw Shark?
The saw of a saw shark is used for hunting and defense, enabling it to stun and capture its prey.
How Does A Sawfish Use Its Saw?
A sawfish uses its saw to locate and stun prey, as well as for maneuvering through the water.
Can The Saw Of A Saw Shark Or Sawfish Harm Humans?
While the saws of both species can be dangerous if provoked, they are not known to intentionally attack humans.
Conclusion
Both the saw shark and the sawfish are fascinating species known for their unique saw-shaped snouts. While they share similarities in appearance, they have distinct differences in their physical features, habitats, and behavior. The saw shark’s smaller size and elongated snout make it more maneuverable and efficient when catching prey, while the sawfish’s larger size gives it a greater striking range.
Their habitats also differ, with the saw shark preferring deeper waters and the sawfish being more commonly found in coastal areas. Additionally, the sawfish is a more social creature, often living in groups, while the saw shark is generally solitary.
Understanding the differences between these two creatures is not only fascinating but also important for their conservation and protection. Both species face threats such as habitat destruction and overfishing, which have led to a decline in their populations. By promoting awareness and implementing conservation measures, we can ensure the survival of these unique creatures and maintain the biodiversity of our oceans.