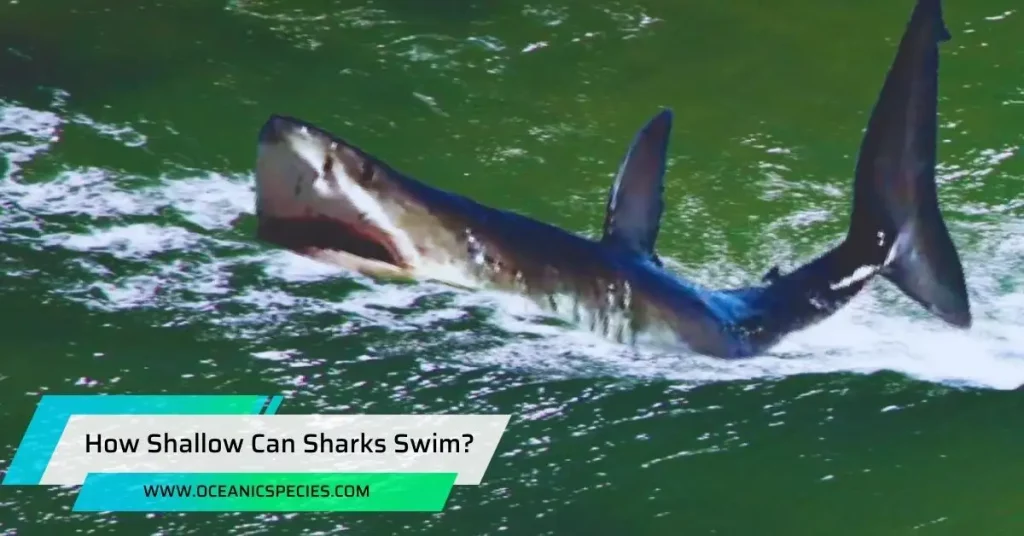
Sharks can swim as shallow as a few inches or even less. In general, sharks can navigate in very shallow waters.
However, their ability to do so depends on the species and their size.
A Brief Introduction To Sharks’ Impressive Swimming Abilities
Sharks have long been known as the apex predators of the ocean, ruling the vast expanse of the deep blue sea. These incredible creatures have adapted over millions of years to become highly efficient swimmers, equipped with a unique set of biological adaptations that enable them to navigate their watery world with ease.
From their streamlined bodies to their powerful tails, sharks possess an impressive array of swimming abilities that truly make them masters of their domain.
Understanding The Biology Of Sharks
To truly appreciate the swimming abilities of sharks, we must delve into their fascinating biology. Here are some key points to consider:
- Streamlined bodies: Sharks have sleek and torpedo-shaped bodies that minimize drag and resistance in the water. This streamlined design allows them to effortlessly glide through the ocean, reaching impressive speeds.
- Powerful tails: One of the most important features of a shark’s swimming prowess is its tail. Composed of strong muscles, the tail propels the shark forward with great force, generating speed and agility in the water.
- Fin-tastic fins: Sharks have several sets of fins that help them navigate and maneuver in the water. The pectoral fins, located on the sides of their bodies, provide lift and stability, while the dorsal fin helps maintain balance and prevents rolling.
- Hydrodynamic skin: The skin of a shark is covered in tiny tooth-like structures called dermal denticles. These denticles not only protect the shark’s skin but also reduce friction and turbulence, enabling smooth and efficient movement through the water.
- Buoyancy control: Sharks possess a unique mechanism known as the swim bladder, which helps them control their buoyancy. By regulating the amount of gas in the swim bladder, sharks can adjust their depth in the water column, assisting them in their quest for optimal swimming efficiency.
The Importance Of Shallow Swimming For Sharks
Sharks, known for their fearsome image and the depths they can reach in the ocean, may surprise you with their ability to navigate shallow waters. In this section, we will uncover the secrets of shallow-water habitats and explore the importance of shallow swimming for sharks.

Unveiling The Secrets Of Shallow-Water Habitats
Shallow-water habitats are often overlooked in favor of the deep sea, but they play a critical role in the life of a shark. Here are some key points to consider:
- Shallow waters provide sharks with a diverse range of prey. From small fish to crustaceans, these nutrient-rich environments offer an abundant food source for sharks to thrive.
- Coral reefs, mangroves, and estuaries are common shallow-water habitats. These areas serve as crucial nursery grounds for many shark species. Juvenile sharks rely on these habitats for protection and feeding, ensuring the future of their populations.
- Shallow waters are teeming with life. Aside from prey, these habitats are home to a variety of fish species, rays, and other marine organisms. The interconnectedness of the ecosystem in shallow waters is essential for maintaining a balance and support system for aquatic life.
The Role Of Shallow Swimming In A Shark’S Life
Shallow swimming serves several important purposes for sharks. Let’s delve into the significance of this behavior:
- Basking in the sun: Some shark species, like the nurse shark, are known to spend time in shallow waters to soak up the sun. This behavior helps regulate their body temperature and aids in digestion.
- Hunting strategy: Shallow waters provide opportunities for sharks to employ different hunting techniques. They can ambush prey from below or even breach the surface to capture fast-swimming fish.
- Mating and courtship: Sharks often gather in shallow waters during mating season. These areas serve as meeting grounds for males and females, allowing for courtship behaviors and successful reproduction.
- Avoiding predators: By swimming in shallow waters, sharks can take advantage of their agility and maneuverability. These habitats provide refuge from larger predators, increasing their chances of survival.
How Shallow Can Sharks Swim?
Known for their incredible power and agility, these apex predators are often associated with deep ocean waters. But have you ever wondered just how shallow can sharks swim?

In this section, we will explore the shallow water zones that various shark species inhabit and reveal the surprising depths these magnificent creatures can navigate.
Shallow Water Zones Explored By Different Shark Species:
Coastal areas:
Many shark species can be found in coastal areas, where shallow waters meet the shoreline. These zones offer an abundant food source and are home to a diverse range of marine life, making them a popular hunting ground for sharks.
Coastal areas provide sharks with ample opportunities to feed, as they can easily prey on fish, seals, sea lions, and other marine animals that frequent these waters. While some sharks prefer deeper waters even in coastal regions, others like the bull shark have been known to venture into extremely shallow waters, sometimes even in rivers or freshwater lakes.
Coral reefs:
Coral reefs are teeming with life, making them an attractive habitat for various shark species. While not all sharks can navigate through the narrow crevices of a coral reef, some, like the nurse shark or the whitetip reef shark, are well adapted to these environments.
Sharks that inhabit coral reefs often rely on the reef itself for food and shelter. They can hide within the reef’s intricate structure and ambush unsuspecting prey that ventures too close. These sharks play an essential role in maintaining the delicate balance of coral reef ecosystems by controlling the population of reef-dwelling prey species.
Estuaries and mangroves:
Estuaries and mangroves are unique ecosystems where freshwater rivers meet the ocean. These areas provide an ideal mix of saltwater and freshwater, creating a diverse environment that supports a wide array of marine and terrestrial life. Sharks like the bull shark are known to venture into estuaries and mangroves, making use of these shallow and nutrient-rich waters to hunt for prey.
These habitats also serve as nurseries for many shark species, providing sheltered areas for their young to grow and develop before venturing out into the open ocean.
Revealing The Surprising Depths Sharks Can Navigate:
Deep dives:
While sharks are commonly associated with deep ocean waters, some species have demonstrated the ability to dive to remarkable depths. For example, the greenland shark has been found at depths of up to 2,200 meters, making it one of the deepest-diving sharks known.
These deep dives allow sharks to explore a different realm of the ocean where unique species reside. It also provides them with access to new food sources that may not be available in shallower waters.
Vertical migrations:
Some shark species, such as the blue shark, are known to undertake vertical migrations. These migrations involve traveling from the surface waters, where they feed during the day, to deeper waters at night.
By venturing into deeper waters, sharks can access different prey species that migrate vertically in the water column. This behavior allows them to optimize their feeding strategies and take advantage of the abundant resources available at different depths.
Factors Influencing Sharks’ Ability To Swim In Shallow Waters
Sharks, often portrayed as deep-sea predators, are actually capable of swimming in shallow waters. Their anatomy and unique adaptations play a crucial role in their ability to navigate these environments effectively. Here are some key points to understand:
- Streamlined body: Sharks possess a sleek and streamlined body shape that minimizes drag, allowing them to move swiftly through the water, even in shallow areas.
- Pectoral fins: Located on either side of their body, the pectoral fins act as wings, providing lift and stability. These fins are particularly useful for maneuvering in shallow waters where agility is crucial.
- Lateral line: Sharks have a sensory structure called the lateral line, which runs along their body. It enables them to detect minute water movements and vibrations, helping them navigate obstacles and locate prey in shallow environments.
- Tails and caudal fins: Sharks’ tails, along with their caudal fins, provide the primary source of propulsion. The shape and flexibility of these fins allow them to generate powerful thrust, enabling efficient movement in shallow waters.
- Ampullae of lorenzini: Ampullae of lorenzini are small electroreceptor organs found on a shark’s snout. They detect electrical fields produced by other living organisms, aiding sharks in hunting and navigation, even in murky and shallow waters.
Environmental Factors Affecting Sharks’ Shallow Swimming Patterns
While sharks possess natural adaptations to swim in shallow waters, various environmental factors can influence their swimming patterns. Here are some key points to consider:
- Water temperature: Sharks are ectothermic creatures, meaning their body temperature is regulated by the surrounding environment. Different species of sharks have specific temperature preferences, which can affect their distribution and movement within shallow waters.
- Salinity: Changes in water salinity can affect sharks’ ability to navigate shallow environments. Some species are adapted to survive in both fresh and saltwater, while others may prefer specific salinity levels.
- Food availability: The presence of sufficient food sources plays a significant role in the distribution and swimming patterns of sharks in shallow waters. They tend to frequent areas with abundant prey, such as spawning grounds or areas teeming with small fish.
- Habitat structure: The physical characteristics of shallow water habitats, such as coral reefs, mangroves, or estuaries, provide essential resources and shelter for sharks. The presence of these structures can influence their swimming patterns and feeding behavior.
- Human activities: Human impact, including coastal development, pollution, and fishing practices, can disrupt sharks’ natural habitats and affect their ability to survive in shallow waters. Overfishing and habitat degradation can lead to reduced prey availability and population decline.
Swimming Techniques Employed By Sharks In Shallow Waters
Sharks are renowned for their sleek bodies and powerful swimming skills. While they are often associated with deep ocean waters, sharks are also adept at navigating shallow areas. In this section, we will explore the swimming techniques employed by sharks in these shallow waters.
Let’s delve into their key characteristics and effortless maneuvers.
Speed And Agility: Key Characteristics Of Sharks’ Shallow-Water Swimming

Sharks are built for speed, making them masters of the open water. Even in shallow areas, they showcase their remarkable agility through the following key characteristics:
- Streamlined body: With their torpedo-shaped bodies, sharks minimize drag and increase efficiency while swimming in shallow waters. This sleek design allows them to navigate with ease and reach impressive speeds.
- Powerful tail fin: Sharks utilize their large, muscular tail fin, called the caudal fin, to propel themselves forward through the water. This tail fin acts as a powerful engine, generating the force needed to maintain their speed and agility.
- Pectoral fins: Located on the sides of their bodies, sharks’ pectoral fins play a crucial role in shallow-water swimming. These fins provide the necessary lift and stability, allowing sharks to maintain balance while maneuvering through the shallows.
- Ampullae of lorenzini: These sensory organs, found in a shark’s head, enable them to detect the electrical fields produced by their prey. This heightened sense allows sharks to react swiftly and accurately, aiding their swift movements even in shallow waters.
Effortless Maneuvers: Uncovering The Techniques Sharks Use In Shallow Waters
While navigating shallow waters may present unique challenges, sharks have evolved specific techniques to effortlessly maneuver through these areas:
- Bottom skimming: Sharks often swim close to the seabed, taking advantage of the reduced water resistance in the shallow depths. They utilize their pectoral fins to glide smoothly above the sandy or rocky bottoms, conserving energy during their journeys.
- Tail slap: In some cases, sharks employ a tail slap maneuver, particularly when chasing prey in the shallows. By forcefully swiping their tails against the water’s surface, sharks create a significant disturbance, disorienting their target and increasing their chances of a successful hunt.
- Quick turns and zigzag movements: To navigate the confined spaces of shallow reefs or rocky areas, sharks employ quick turns and zigzag movements. This agility allows them to swiftly change directions and ambush unsuspecting prey or evade potential threats.
- Burst speeds: Sharks possess the impressive ability to accelerate rapidly in short bursts, no matter the depth of the water. This burst of speed allows them to strike with precision while hunting in shallow areas, ensuring they swiftly catch their prey before it can escape.
Unique Shallow-Water Behaviors Of Sharks
Sharks, with their sleek bodies and terrifying reputation, are known to be creatures of the deep sea. However, many people are not aware of the unique behaviors exhibited by sharks in shallow waters. In this section, we will explore the hunting strategies employed by sharks in shallow waters as well as the significance of shallow waters for their reproduction and breeding grounds.
Hunting Strategies In Shallow Waters
Sharks are not limited to the depths of the ocean when it comes to hunting. They have adapted to navigate and thrive in the shallows, showcasing impressive hunting strategies. Here are some key points to consider:
- Ambushing prey: In shallow waters, sharks often utilize the element of surprise. They patiently wait, camouflaged against the seabed or vegetation, before launching swift attacks on unsuspecting prey.
- Patrolling coastal areas: Many shark species, such as bull sharks and tiger sharks, patrol the shallow waters close to shore. They take advantage of the abundant food sources found in coastal ecosystems, including fish, crustaceans, and even seabirds.
- Exploring tidal pools: Some sharks, like the port jackson shark, are specifically adapted to explore tidal pools during low tide. These pools become isolated habitats, trapping various marine organisms, which the sharks take advantage of as an easy food source.
- Utilizing structure and currents: Sharks in shallow waters often rely on natural formations such as rocky outcrops, reefs, and even man-made structures like piers and jetties. These structures create ideal ambush points for sharks, where they can swiftly navigate and exploit the currents to their advantage.
Reproduction And Breeding Grounds: The Significance Of Shallow Waters For Sharks
Shallow waters play a crucial role in the reproduction and breeding processes of sharks. Here are some key points to consider:
- Courtship rituals: Many shark species engage in elaborate courtship rituals that take place in shallow waters. These rituals often involve visual displays and physical interactions between males and females, vital for successful reproduction.
- Nursery areas: Shallow waters provide ideal nursery areas for young sharks. These protected environments offer an abundance of food and protection from larger predators, ensuring the survival and growth of the next generation.
- Mating aggregations: Certain shark species, such as the lemon shark, form large mating aggregations in shallow waters. These aggregations bring together males and females, increasing the chances of successful reproduction.
- Sensory acuity: Shallow waters offer optimal conditions for sharks to utilize their highly developed senses. From detecting pheromones released by potential mates to using electroreception to find prey, sharks rely on the sensory cues present in shallow waters.
Challenges Faced By Sharks In Shallow-Water Environments
These shallow-water habitats pose unique challenges for sharks, primarily due to human interactions and their impact on the ecosystem. In this section, we will explore the challenges faced by sharks in shallow-water environments, as well as the conservation efforts aimed at protecting these magnificent creatures and their habitats.

Human Interactions And Their Impact On Sharks’ Shallow-Water Habitat
- Overfishing: Shark populations are threatened by overfishing, primarily driven by the demand for their fins, meat, and other products. This unsustainable practice disrupts the delicate balance of the shallow-water ecosystem, impacting the prey availability and overall health of the habitat.
- Bycatch: Sharks often become unintentional victims of fishing activities targeting other species. This incidental catch, known as bycatch, leads to significant mortality rates among sharks, further contributing to their declining populations.
- Habitat degradation: Human activities such as coastal development, pollution, and destructive fishing practices result in the degradation of shallow-water habitats. Habitat loss and destruction not only directly affect the sharks but also disrupt the food chain and the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Sharks And Their Shallow-Water Ecosystems
- Fishing regulations: Implementing and enforcing strict fishing regulations, including size and catch limits, can help conserve shark populations. By reducing overfishing, regulations aim to maintain a sustainable balance in the ecosystem and protect shallow-water habitats.
- Protected areas: Designating marine protected areas (mpas) can provide safe havens for sharks and their habitats. Mpas help control human activities and provide space for the recovery and conservation of shark populations.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of sharks in the ecosystem is crucial. Educating the public about the role sharks play in maintaining a healthy marine environment can inspire conservation actions and foster a sense of stewardship.
- Sustainable fishing practices: Encouraging the adoption of sustainable fishing practices, such as using shark-friendly gear and releasing bycatch unharmed, can significantly reduce the impact on shark populations in shallow-water environments.
- Research and monitoring: Continual research and monitoring efforts are essential to understand the behaviors, migration patterns, and population dynamics of sharks in shallow-water ecosystems. This knowledge can inform targeted conservation strategies and help in the long-term protection of these habitats.
Conclusion: Awe-Inspiring Swimming Abilities Of Sharks Unveiled
Sharks, one of the most mesmerizing creatures in the ocean, possess truly incredible swimming abilities. Adapted to various aquatic environments, these apex predators have evolved specific characteristics that enable them to navigate shallow waters with ease. Let’s uncover the awe-inspiring adaptations that make sharks such efficient shallow swimmers:
- Streamlined body shape: A shark’s sleek and streamlined body allows it to move efficiently through water, minimizing drag and maximizing speed.
- Pectoral fins: Positioned on either side of their body, a shark’s pectoral fins provide stability and control during rapid movements, enabling precise maneuverability in shallow depths.
- Tail fin (caudal fin): Incredibly powerful, a shark’s tail fin propels them forward, generating the necessary thrust to swiftly navigate through shallow waters.
- Dorsal fins: Sharks have multiple dorsal fins, including a prominent first dorsal fin, which aids in stability and prevents rolling during fast swimming.
- Ampullae of lorenzini: These specialized sensory organs located on a shark’s snout allow them to detect electrical fields emitted by potential prey, assisting in navigation and hunting in shallow habitats.
- Lateral line system: Consisting of tiny, specialized sensory cells, a shark’s lateral line system is responsible for detecting vibrations and changes in water pressure, enabling them to sense movement and find prey, even in shallow waters.
- Slit-like spiracles: Some bottom-dwelling sharks have specialized structures called slit-like spiracles located behind their eyes. These allow them to draw in water for respiration, even when buried in the sand.
Appreciating The Wonders Of Nature: The Amazing World Of Sharks
Understanding the incredible adaptations that sharks possess for shallow swimming reveals just how fascinating and awe-inspiring these creatures truly are. As we appreciate the wonders of nature, here are a few notable points to consider about the amazing world of sharks:
- Exceptional speed: Sharks can reach impressive speeds, with some species capable of swimming up to 60 miles per hour (97 km/h). Their agility and speed make them formidable hunters in shallow environments.
- Acute senses: Sharks have highly developed senses, including a keen sense of smell, excellent vision, and highly sensitive hearing. These heightened senses allow them to navigate shallow waters efficiently and locate prey with precision.
- Varied diet: While some sharks primarily feed on fish, others indulge in mollusks, crustaceans, seals, or even other sharks. Their adaptability to different food sources highlights their ability to thrive in various shallow habitats.
- Remarkable lifespan: Sharks can live for several decades, showcasing their ability to survive and adapt to changing environments over extended periods. They are resilient creatures, perfectly suited for shallow waters.
- Importance in ecosystems: As apex predators, sharks play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. By regulating populations of prey species, they help ensure the health and stability of shallow habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Sharks Only Swim In Deep Waters?
No, sharks are found in various depths of water, including shallow coastal areas.
Can Sharks Survive In Shallow Water?
Yes, sharks can survive in shallow water as they have evolved to adapt to different environments.
Why Do Sharks Swim Close To Shore?
Sharks swim close to shore in search of food sources, such as fish and seals.
Are There Dangerous Sharks In Shallow Waters?
While some sharks can be found in shallow waters, the majority of them pose little threat to humans.
Conclusion
Understanding how shallow sharks can swim is not only fascinating but also crucial for various reasons. It is evident that these impressive creatures are capable of navigating shallow waters due to their unique adaptations and behaviors. Their ability to swim in shallow areas allows them to expand their habitat range, access new food sources, and potentially avoid predation.
With the help of advanced research techniques, scientists have been able to uncover intriguing insights into the depths to which different shark species can venture. However, it is important to continue studying and protecting these incredible creatures to ensure their survival and maintain the delicate balance of our oceans.