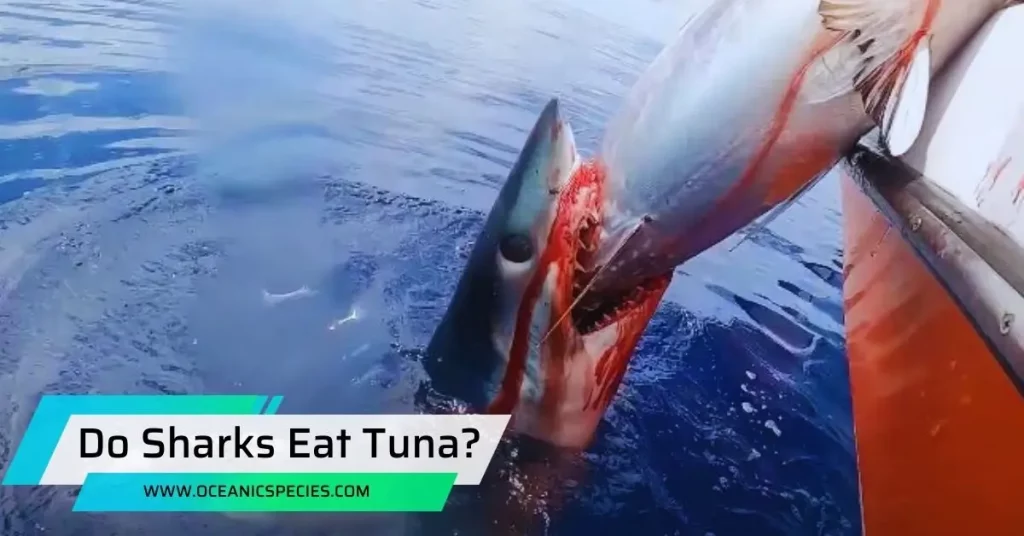
Yes, sharks do eat tuna. Sharks are known to be opportunistic feeders and will consume a wide range of prey, including tuna.
While sharks have a diverse diet and can consume various types of prey, including fish, marine mammals, and even other sharks, tuna is certainly among the menu options for these apex predators. We will explore the relationship between sharks and tuna, shedding light on their feeding habits and providing insights into the dynamic ecosystem of the ocean.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the dietary preferences of these mighty predators, read on to discover more about sharks and their appetite for tuna.
The Relationship Between Sharks And Tuna
Tuna is indeed a highly prevalent prey of sharks, despite the common misconception that suggests otherwise. Understanding the relationship between these two marine creatures sheds light on the intricate dynamics of ocean ecosystems and the role sharks play as top predators.
Tuna: A Highly Prevalent Prey Of Sharks
Sharks are fascinating creatures that have been the subject of curiosity and fear for centuries. These apex predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems, and their diet consists of a wide variety of prey. One such prey species that often falls victim to sharks is the tuna, a highly prevalent food source for these formidable hunters.
Here are some key points to understand the relationship between sharks and tuna:
- Sharks are opportunistic feeders and have a diverse diet that varies depending on their species and habitat. Tuna, with its abundance in many oceanic regions, makes for a significant portion of a shark’s diet.
- Tuna are fast-swimming fish known for their muscular bodies and ability to cover long distances. This speed and agility, however, do not always protect them from becoming the meal of choice for sharks.
- Sharks often target tuna due to their high energy content and availability. Tuna packs a nutritional punch and can provide sharks with essential proteins and fats necessary for their survival and energy needs.
- Some species of sharks, such as the great white shark, are highly skilled hunters capable of ambushing their prey. These stealthy predators use their incredible speed and acute senses to track down tuna in the vast oceanic expanse.
- The relationship between sharks and tuna is not a one-sided affair. Tunas have evolved their own set of adaptations to avoid falling victim to sharks, such as their streamlined bodies, which facilitate swift underwater movement.
- It is important to note that not all sharks eat tuna, and their diet varies depending on their respective habitats and available prey. However, in regions where tuna populations are abundant, it’s not uncommon for sharks to include them in their diet.
The Common Misconception: Sharks Do Not Eat Tuna
Contrary to what some people may believe, sharks do indeed eat tuna. This misconception may arise from the lack of visual evidence or an incomplete understanding of a shark’s feeding behavior. However, extensive research and observation have confirmed that tuna forms a significant part of many shark species’ diet.
The notion that sharks do not eat tuna may stem from the fact that humans often associate tunas with our own fishing practices. While it’s true that humans catch tuna for consumption, sharks have a different set of hunting strategies and preferences. Additionally, the vastness and depth of the ocean make it difficult for humans to witness every encounter between sharks and tuna. It’s essential to consider that many shark feeding behaviors occur far from the reach of human observation.
To further complicate matters, not all tuna species are equally targeted by sharks. Different shark species have their own hunting techniques and prey preferences, which may lead to variations in the selection of tuna species.
Understanding the feeding habits of sharks
Sharks are apex predators that play a vital role in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. By regulating prey populations, they ensure a balanced ecological structure. Sharks have evolved over millions of years, developing a wide range of feeding strategies and adaptations to optimize their hunting success. These fascinating creatures employ a combination of ambush tactics, swift pursuit, and sensory perception to locate and capture their prey.
While many sharks are known for their ability to take down large prey, they also exhibit a flexible feeding behavior that allows them to adapt to different food sources based on their availability. The feeding habits of sharks can vary depending on factors such as species, size, habitat, and ecological conditions. Some species primarily feed on smaller prey like fish and squid, while others can tackle larger animals such as seals or marine mammals.
Sharks have an incredible ability to detect even the faintest traces of prey in the water, thanks to their highly developed senses. Their acute sense of smell allows them to detect blood and bodily secretions over vast distances, while their electroreceptive organs help them locate hidden or camouflaged prey.
Debunking The Myth: Sharks Do Eat Tuna
It is clear that sharks do, in fact, eat tuna. Scientific studies, observations, and real-life instances all provide evidence of this predatory relationship. The myth that sharks do not consume tuna can finally be put to rest, allowing us to appreciate the fascinating dynamics between these oceanic creatures.

Examining Scientific Studies And Observations
In-depth studies conducted by marine biologists have revealed that many shark species do indeed include tuna in their diet. Scientists have observed sharks feeding on schools of migrating tuna, indicating a clear predatory relationship. Tracking studies using satellite tags have shown that sharks actively swim alongside tuna, suggesting that they are actively hunting their prey.
Predatory Behaviors: Sharks’ Ability To Consume Tuna
Sharks possess a remarkable ability to consume large prey, including tuna, due to their unique physiological features. Their razor-sharp teeth are perfectly adapted to tear through the tough skin and flesh of tuna, allowing for efficient consumption. Sharks’ powerful jaws and strong bite force enable them to break through bones and swallow large chunks of prey. Some shark species, like the great white shark, are known to breach the surface while hunting, launching themselves out of the water to catch their prey, which may include tuna.
Case Studies: Instances Of Sharks Consuming Tuna
One fascinating case study involves the annual tuna migration in the mediterranean sea. Bluefin tuna, prized for their succulent flesh, are known to attract many predators, including various shark species. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
- In a study conducted off the coast of gibraltar, researchers witnessed blue sharks hunting schools of bluefin tuna, exhibiting distinct predatory behavior.
- Further south in the mediterranean, thresher sharks have been observed preying on schools of tuna, using their long tails to strike and stun their victims before devouring them.
- Additionally, oceanic whitetip sharks are notorious for their opportunistic feeding habits and have been observed scavenging on dead or injured tuna.
Factors Affecting Shark-Tuna Interactions
Sharks and tuna have complex interactions influenced by factors such as habitat, size, and environmental impacts. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of ocean ecosystems.

Let’s explore the factors that affect shark-tuna interactions.
Habitat And Distribution: Where Sharks And Tuna Coexist
Sharks and tuna can be found in various ocean habitats around the world, including coastal waters and open ocean areas. Tuna often swim in the upper water column, while sharks tend to occupy different depths, ranging from shallow coastal regions to deeper waters. Some species of sharks and tuna share common habitats, such as the blue shark and the yellowfin tuna. This overlap increases the chances of their interactions.
Size And Species: Sharks’ Preference For Different Tuna
Sharks have diverse preferences when it comes to the species and size of tuna they consume. Factors such as the shark’s size, hunting behavior, and anatomical adaptations play a crucial role in their selection. Larger sharks may target larger species of tuna, such as the yellowfin tuna or the bigeye tuna, due to their size advantage and higher energy requirements.
Smaller sharks may go after smaller species of tuna, such as the skipjack tuna or the bullet tuna, which are more easily accessible and abundant. The preferences of sharks can also vary based on their individual hunting techniques, with some sharks targeting injured or weaker tuna.
Environmental Impact: Overfishing And Shark Depletion
Overfishing of tuna can have a significant impact on shark populations. When tuna populations decline due to excessive fishing, it disrupts the food chain and affects the availability of prey for sharks. The depletion of shark populations can also occur as a result of bycatch, where sharks get unintentionally caught in fishing nets and gear targeting tuna. The loss of sharks in the ecosystem can lead to imbalances in the marine environment, as they play a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of coral reefs and other habitats.
Conservation Efforts To Protect Sharks And Tuna
The conservation efforts to protect sharks and tuna involve implementing sustainable fishing practices, implementing shark conservation measures, and fostering collaboration between fisheries and conservationists. By preserving the delicate balance between these apex predators and commercially important species, we can ensure the long-term stability of our oceans and the diverse marine life they support.
Let’s explore the conservation efforts made to protect both sharks and tuna, as well as the sustainable fishing practices implemented.
Sustainable Fishing Practices: Balancing Tuna Harvesting
Sustainable fishing practices play a crucial role in ensuring the delicate balance between harvesting tuna and preserving shark populations. Here are some key points to consider:
- Bycatch reduction: Bycatch refers to unintentional capture of non-target species during fishing operations. Implementing measures such as using fish aggregating devices (fads) with escape hatches for sharks or modified fishing gear significantly reduces bycatch, minimizing harm to sharks while targeting tuna.
- Closed areas and seasons: Establishing closed areas or seasons for fishing can provide the much-needed respite for both tuna and shark populations. These restrictions allow fish stocks to replenish and enhance the overall sustainability of the fishing industry.
- Size and bag limits: Setting specific size and bag limits for tuna catches helps protect juvenile and breeding individuals, allowing them to reach maturity and sustain their populations. These regulations indirectly benefit sharks by maintaining the overall health of the marine ecosystem.
Implementing Shark Conservation Measures
Recognizing the importance of sharks in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems, various conservation measures have been implemented to safeguard their populations. Let’s delve into the key strategies:
- Banning shark finning: Many countries have enforced strict regulations against shark finning, a practice where sharks’ fins are removed and the rest of the body discarded. This ban prevents overexploitation and promotes responsible fishing practices that prioritize the conservation of sharks.
- Protected species: Designating certain shark species as protected not only safeguards their existence but also helps to create awareness about their ecological significance. These protective measures ensure that sharks can fulfill their role as apex predators, thereby maintaining the balance within the oceanic food chain.
- Global initiatives: Collaborative efforts like the convention on international trade in endangered species of wild fauna and flora (cites) and the international union for conservation of nature (iucn) shark specialist group actively work towards the conservation of sharks by advocating for stronger regulations and protection across the globe.
Collaboration Between Fisheries And Conservationists
In an effort to ensure the survival of both sharks and tuna, collaboration between fisheries and conservationists has become paramount. Here are notable collaborative approaches:

- Research and data sharing: Fisheries and conservationists work hand in hand, sharing research findings and data to better understand the dynamics between sharks and tuna. This collaboration aids in developing effective conservation strategies that mitigate negative impacts on both species.
- Joint conservation initiatives: Joint efforts between fishermen and conservation organizations encourage responsible fishing practices and raise awareness about the importance of protecting sharks and tuna. These initiatives foster a sense of shared responsibility towards marine conservation.
- Educational programs: Collaborations often involve educational programs aimed at educating fishermen and the public about the ecological significance of sharks and tuna. These programs serve to dispel misconceptions and encourage sustainable fishing practices that benefit both species.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Relationship Between Sharks And Tuna?
Sharks and tuna have a predator-prey relationship, where sharks hunt and feed on tuna.
Are Tuna Safe From Shark Attacks?
Tuna have developed strategies, such as their speed and agility, to evade shark attacks. However, they are still vulnerable.
Why Do Sharks Find Tuna So Appealing?
Sharks find tuna appealing due to their high energy and nutritional content, making them a valuable food source.
Are There Any Other Factors That Affect The Interaction Between Sharks And Tuna?
Environmental factors, such as location and seasonality, can impact the interaction between sharks and tuna, as well as their abundance and availability.
Conclusion
Sharks and tuna have long been associated as hunter and prey, with the notion that sharks invariably devour tuna whenever they cross paths. However, the reality is much more nuanced than this oversimplified narrative. While it is true that some species of sharks do eat tuna, it is not the case for all sharks.
Sharks have diverse dietary preferences, and their eating habits largely depend on their species, habitats, and availability of food. Additionally, the size of the tuna and the size of the shark are significant factors in determining whether a shark would consume it or not.
Moreover, the behavior, speed, and agility of the tuna play an important role in deterring shark attacks. It is crucial to understand the complex relationship between sharks and tuna to avoid perpetuating misconceptions about these majestic creatures.